Page 21 - CJSeptember25
P. 21
the median composition age in 2017–2019 (87 and 58). led to the question of whether another variable in the
Notably, these three schools all saw faculty changes oc- dataset, such as a work’s accompaniment status or lan-
cur in their programs during the years between the two guage, might serve as a proxy for composition difficulty.
time periods studied. These results suggest major dif- While accompaniment status (accompanied vs. un-
ferences among graduate choral conducting programs accompanied) did not show any correlation with com-
regarding the extent to which they program historical position difficulty under any of the three measures
music, and that these determinations are largely tied to used, language did. Among the works in the dataset,
the faculty member(s) who lead(s) each program rath- works performed in a language other than English had
er than being inherent to the particular school or pro- a significantly higher average difficulty score under all
gram. three measures than did works performed in English,
suggesting that English vs. non-English works might be
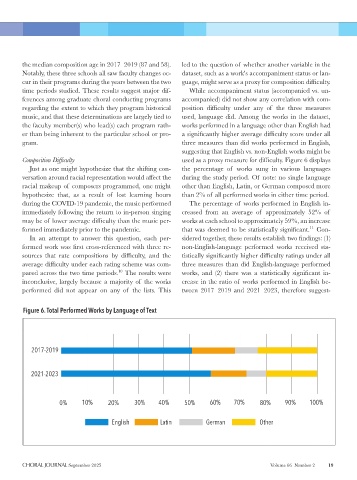
Composition Difficulty used as a proxy measure for difficulty. Figure 6 displays
Just as one might hypothesize that the shifting con- the percentage of works sung in various languages
versation around racial representation would affect the during the study period. Of note: no single language
racial makeup of composers programmed, one might other than English, Latin, or German composed more
hypothesize that, as a result of lost learning hours than 2% of all performed works in either time period.
during the COVID-19 pandemic, the music performed The percentage of works performed in English in-
immediately following the return to in-person singing creased from an average of approximately 52% of
may be of lower average difficulty than the music per- works at each school to approximately 59%, an increase
11
formed immediately prior to the pandemic. that was deemed to be statistically significant. Con-
In an attempt to answer this question, each per- sidered together, these results establish two findings: (1)
formed work was first cross-referenced with three re- non-English-language performed works received sta-
sources that rate compositions by difficulty, and the tistically significantly higher difficulty ratings under all
average difficulty under each rating scheme was com- three measures than did English-language performed
pared across the two time periods. The results were works, and (2) there was a statistically significant in-
10
inconclusive, largely because a majority of the works crease in the ratio of works performed in English be-
performed did not appear on any of the lists. This tween 2017–2019 and 2021–2023, therefore suggest-
Figure 6. Total Performed Works by Language of Text
2017-2019
2021-2023
0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% 70% 80% 90% 100%
English Latin German Other
CHORAL JOURNAL September 2025 Volume 66 Number 2 19