Page 58 - April.indd
P. 58
muscular tension also allows the lar- phasizes a singer’s individual sound overtone series (Image 3).
ynx to maintain a relatively low po- by expressing a wide range of har- This image reinforces Scott Mc-
sition and helps other muscles in the monics, as well as the fundamental, Coy’s observation that “spectral
throat to relax, creating more space similar to the style of singing used in analysis reveals strong harmonic
and further de-emphasizing upper Sacred Harp music. Another exam- overtones as high as 10,000hz, very
harmonics. This essentially creates ple of the Wide Spectrum sound is diff erent from the classical ideal, in
an [u] space in the throat regardless Musical Theater Belting, traditional- which the harmonics above 4,000hz
of what vowel the oral cavity shapes. ly defined as using the ‘chest voice’ (a are sharply attenuated.” Notice,
8
term often used to describe a feeling in particular, how strong the upper
of resonance in the chest when more harmonics are, even compared to
Wide Spectrum mass of the vocal folds is touching) the fundamental. In this case, the
of Emphasized Harmonics in the middle to upper middle part 2nd through 4th harmonics are
(Wide Spectrum) of the range. Note, for instance, this quite a bit stronger than the funda-
In stark contrast to the Funda- example of Musical Theater Belting mental, and signifi cant harmonic
mental Dominant sound, which cre- by Broadway singer Idina Menzel presence continues all the way up
ates a timbral homophony of voices as she sings the climactic high note to nearly 10,000hz, a result of the
by de-emphasizing upper harmonics in Let It Go, from the Disney musical intense sub-glottal pressure during
9
and focusing on the fundamental Frozen. Here you can see the broad Musical Theater Belting. The de-
pitch, Wide Spectrum singing em- set of harmonics in all parts of the gree to which the upper harmonics
are attenuated reveals the diff erence
between what is referred to in musi-
cal theater parlance as a Belt vs. Legit
singing. The Legit quality attenuates
the highest harmonics, making it
closer in timbre to Bel Canto sing-
ing. The effect can be achieved with
some additional increase in vocal
fold mass (shortening/thickening of
the vocal folds) in combination with
shortening parts of the vocal tract,
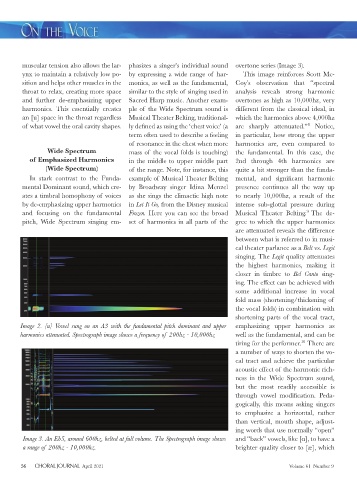
Image 2. [u] Vowel sung on an A3 with the fundamental pitch dominant and upper emphasizing upper harmonics as
harmonics attenuated. Spectrograph image shows a frequency of 200hz - 10,000hz well as the fundamental, and can be
10
tiring for the performer. There are
a number of ways to shorten the vo-
cal tract and achieve the particular
acoustic effect of the harmonic rich-
ness in the Wide Spectrum sound,
but the most readily accessible is
through vowel modifi cation. Peda-
gogically, this means asking singers
to emphasize a horizontal, rather
than vertical, mouth shape, adjust-
ing words that use normally “open”
Image 3. An Eb5, around 600hz, belted at full volume. The Spectrograph image shows and “back” vowels, like [ɑ], to have a
a range of 200hz - 10,000hz. brighter quality closer to [æ], which
56 CHORAL JOURNAL April 2021 Volume 61 Number 9