Page 57 - April.indd
P. 57
that most closely emulates a “pure”
tone, a sound strongly emphasiz-
ing the fundamental pitch, with the
upper harmonics signifi cantly less
5
present. Much like blowing over a
[ a ] partially filled bottle, the resonant
frequencies emphasized in a sung
pitch will lower as the open space
expands. In the voice, this occurs by
widening and lengthening the vocal
tract. Typically, singers achieve this
by creating a more vertical, rather
than horizontal space in the mouth,
regardless of what vowel is being
[ e ] sung, and maintaining a low laryn-
geal position (Image 2 on page 56).
This sound eff ectively empha-
sizes the fundamental pitch, which
is the lowest frequency present, al-
lowing a group of singers to easi-
ly create a timbrally homophonic
sound. For many in the choral
6
[ i ] world, the Fundamental Dominant
timbre is considered the default and
desired “choral tone” and is similar
to the sound often used in Western
renaissance music because it helps
maintain the clarity of individual
lines in polyphonic music, even in a
highly reverberant space. Reducing
[ o ] the amount of vibrating vocal fold
mass also helps de-emphasize upper
harmonics. When the folds stretch
and tilt on their edges, similar to
what happens when singing in fal-
setto, less of the vocal folds vibrate,
[ u ] exciting less air. Because the vocal
folds tend to stretch and thin as one
sings higher, Fundamental Domi-
nant singing is easiest to achieve in
the upper-middle part of a singer’s
tessitura. The Fundamental Domi-
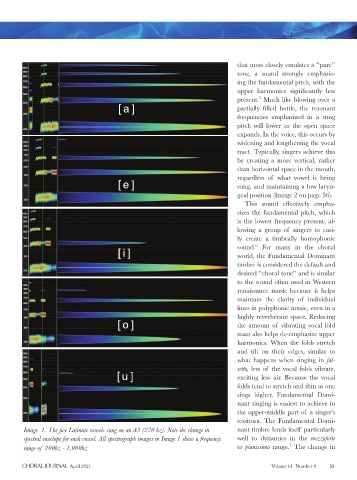
Image 1. The fi ve Latinate vowels sung on an A3 (220 hz). Note the change in nant timbre lends itself particularly
spectral envelope for each vowel. All spectrograph images in Image 1 show a frequency well to dynamics in the mezzoforte
7
range of 200hz - 1,000hz to pianissimo range. The change in
CHORAL JOURNAL April 2021 Volume 61 Number 9 55